
Sharipov Rustam Hasanovich
Kazakh-British Technical University, Republic of Kazakhstan
Title: Application of combined electrochemical reactions for extraction of metals from metal- containing waste
Biography
Biography: Sharipov Rustam Hasanovich
Abstract
The method of application of combined electrochemical reactions is designed for the purpose of obtaining a leaching agent and extraction of metals into a solution from various raw materials in the volume of one reactor. In our experiments, the initial solution was a solution of NaOH. As a source of sulfur for the production of leaching reagents, a sulfur-graphite electrode was used. A study of the electrochemical leaching of metals was carried out in a thermostatic reaction cell. In this case, a sulfur-graphite electrode (SGE) was used as a cathode, and graphite served as an anode. When metals were extracted into the solution, it was shown that practically all physico-chemical factors influence the leaching process, and the microstructure of inorganic aqueous solutions should be considered as one of the important parameters of the technological process. It is shown that the characteristics of solutions vary not only from the change in the concentration of dissolved substances, but also when all the physico-chemical conditions for the leaching of metal-containing raw materials change. We carried out experiments on the transfer into the solution of metals from alloys 1: chemical composition %: Pb - 47.52, Bi - 46.31, Cd - 6.17; from alloy 2 chemical composition %: Cd - 18.83, Ti - 16.93, Ag - 15.49, Sn - 13.28, V - 6.07, Co - 0.11, Ni - 2.18 , Cu - 3.54, Mn - 3.71, Fe - 5.79, Pb - 1.19 and from brass: chemical composition %: Cu - 58.65, Zn - 39.79, Pb - 1.34, Cr - 0.06, N i - 0.05, Nb - 0.11. For example, the degree of silver recovery during electroleaching for 6 hours increases with a NaOH concentration of 0.2 M to 8.2%, 0.5 M to 8.2%, 1.0 M to 12.2%, 2.0 M to 12.6%. For tin, 0.2 M is 6.9%, 0.5 M is 7.6%, 1.0 M is 7.8%, 2.0 M is 8.0%. To achieve the optimum extraction value, studies are continuing to determine the structure of compounds in metallic alloys. Studies have shown that, with optimal technical design, the method of combined electrochemical reactions can be applied to any type of metal-containing raw material.
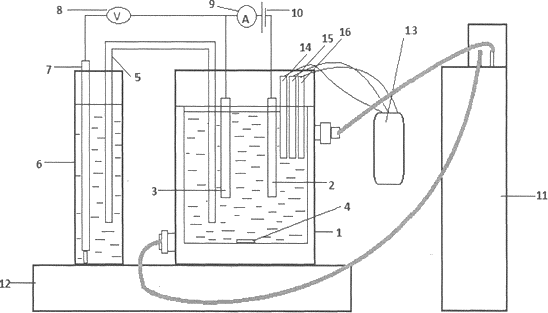
Figure 1: Schematic of an electrochemical cell for leaching.
1 - cell; 2 - graphite electrode; 3 - sulfur/graphite electrode; 4 - a magnet for magnetic stirrer; 5 - a glass bridge; 6 - glass with sodium hydroxide; 7 -silver chloride electrode; 8 - universal voltmeter; 9 - Amperemeter; 10 - power supply; 11 - thermostat; 12 - magnetic stirrer; 13 - multiparameter measuring device (Sens Ion 156); 14 - an electrode for measuring the pH of the medium; 15 - electrode for measuring the concentration of dissolved oxygen; 16 - electrode for measuring the electrical conductivity.
