
Laurentiu Spiridon
Institute of Biochemistry of the Romanian Academy, Romania
Title: Generalized coordinates hybrid Monte Carlo using high speed robotics algorithms
Biography
Biography: Laurentiu Spiridon
Abstract
Simulations of large molecules, like proteins and DNA, are crucial for understanding chemical processes, relevant for medicinal and biochemical applications. As the information about macromolecular systems is accumulating from different types of experimental analysis the studied systems become larger and more complex – e. g. multimeric proteins - making their simulation ever more difficult. Even for simple systems, covering the conformational space while sampling from their proper Boltzmann distribution has proven challenging despite the recent increase in the computational power such as GPU (graphics processing unit) acceleration. One of the reasons for this drawback is that samplers that explore all the thermally accessible configuration space often become trapped in local minima. One way to overcome this is to use holonomic constraints on high-frequency degrees of freedom and group atoms into rigid bodies. One easy way to keep the constraints without imposing additional forces is to give up the Cartesian coordinates and encode the system in an alternate set of generalized coordinates such as BAT coordinates. However, when using arbitrary sets of generalized coordinates for low-frequency degrees of freedom solving the equations of motion requires the costly O(n3) inversion of the mass metric tensor. One solution is to use Jain spatial operator algebra (SOA) developed for robotics which allows to carry this inversion with O(n) complexity. Using recent generalizations of the equipartition principle, Fixman potential and Jain SOA in hybrid Monte Carlo trials to simulate molecular systems in generalized coordinates we were able to reproduce the Boltzmann distribution by drawing highly uncorrelated samples. Furthermore, by mixing fully flexible and random rigid body dynamics, we can achieve ergodicity by stratified sampling. The software needed for the abovementioned type of simulations is freely available online packed in a user-friendly easy to install package called Robo Sampling.
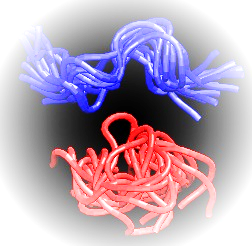
Figure 1. Regular MD (blue) vs GCHMC (red) simulations of a 9 amino acids tyrosinase peptide - YMD.
